Abstract
Introduction:
Grey zone lymphoma (GZL) with an intermediate morphology between classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) and diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) (especially primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma (PMBCL)), entered the WHO classification in 2008. A less frequently described phenomenon, called sequential lymphoma (Seq Ly) corresponds to the occurrence of CHL after DLBCL/PMCBL, or vice/versa during the follow-up (FU). The aim of this study was to describe clinico-pathological characteristics of Seq Ly treated in the rituximab era.
Methods:
Within the LYSA-P (lymphoma study association pathology group) and LYMPHOPATH network, we retrospectively collected 233 cases suspected to be GZL: after central review 139 were classified as true GZL, 10 as composite lymphoma, 20 (12%) as Seq Ly. Among these 20 Seq Ly, characteristics and outcome were available for 18 patients (pts) presented in this analysis. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from time of initial diagnosis or time of 2nd lymphoma diagnosis (OS2) to death of any cause.
Results:
Initial diagnosis was CHL in 15 cases and PMBCL in 3 cases with typical morphology and immunophenotype for each entity. Among the 15 CHL, 4 had DLBCL as 2nd occurrence, 10 PMBCL and 1 GZL with CHL-like morphology (strong and diffuse expression of CD20 on all tumor cells). Among the 3 PMBCL, all had a CHL as 2nd occurrence. At diagnosis, median age was 30 y (16-80), 11/18 (61%) were women. Sixteen patients (89%) had a mediastinal involvement, 7/18 (39%) a stage III/IV Ann Arbor disease with extra nodal localization(s) in 5 cases. Bulky disease was reported in 12/18 patients (66%) and 7/18 (39%) had a high (2-3) age adjusted IPI (international prognostic index) score. In 5/18 cases (28%), the site of 2nd biopsy corresponded to a site that was not involved at diagnosis.
In 13/18 (72%) pts, Seq Ly diagnosis was made in a context of early disease progression during or after initial treatment (early Seq Ly): 4 with progressive disease during therapy, 5 with a partial response (PR) at the end of 1st line therapy, and 4 an early relapse after CR to 1st line (2nd biopsy performed at 1, 3, 5 and 8 m after CR for these cases). For these early Seq Ly, the initial diagnosis was CHL in 11 cases and PMBCL in 2 cases. The remaining 5/18 Seq Ly pts presented a late 2nd lymphoma occurrence (late Seq Ly). Indeed, 4 (3 CHL and 1 PMBCL at diagnosis) had the 2nd biopsy at 18, 27, 30, 69 m after initial CR and 1 (CHL at diagnosis) after an extended PR of 45 m. After a median follow-up of 73 m (range 22-180 m), 8 pts had died. The median OS was not reached and the 5-y OS estimate was 54%. The median OS2 was 22 m and 5y OS2 estimate was 49%.
For salvage, 16 pts received chemotherapy, 14 with rituximab. Two pts (1 late and 1 early Seq Ly of 80 and 30 y respectively) received radiation only and are alive after 79 and 13m of FU since the second biopsy. Eleven patients had an intensive consolidation followed by auto (N=7) and/or allotransplant (N=5). There was no difference in outcome between patients treated with and without transplant after salvage (3 y-OS2 46% vs. 57% respectively), and with or without rituximab (3 y-OS2 42% vs. 50% respectively).
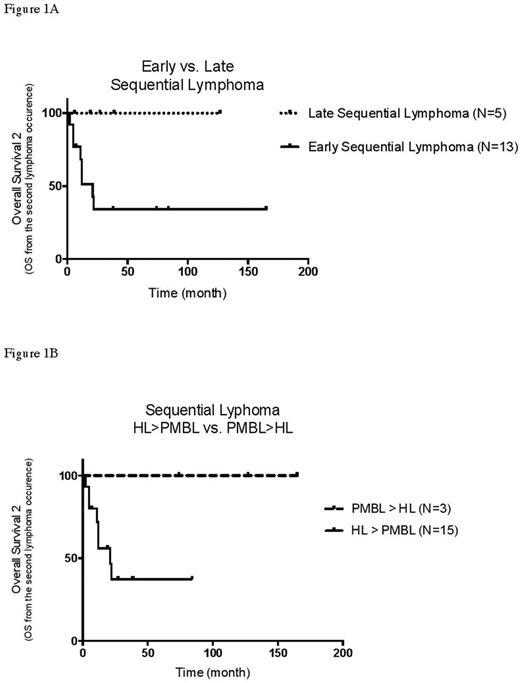
The 13 pts with an early Seq Ly had a poor outcome with a median OS2 of 21 m and 8 deaths. Among the 5 pts with an early Seq Ly still alive, 4 did not experience any relapse within 2 y from salvage (FU: 74, 84, 38, 165 m). For salvage, 2 of these 4 long term disease free survivors had received an ASCT, 1 an allotransplant and 1 radiation only. On the contrary to early Seq Ly, none of the 5 pts with a late Seq Ly had died after a median FU of 27 m after 2nd biopsy (figure 1A). Finally, no primary diagnosed PMBCL pts (N=3) had died (FU of 74, 127 and 165 m after 2nd biopsy (figure 1B)). On the opposite, among the 15 pts with a primary CHL followed by PMBCL, 8 had died and the median OS2 was only 21 m.
Conclusion:
Pts with an early progression during initial treatment (early Seq Ly) represent the majority of Seq Ly cases (72%) and have a poor outcome. With the limitation of the small number of pts, Seq Ly after PMBCL initial diagnosis appears to have a better outcome than Seq Ly after primary CHL. This data suggest that new biopsies for CHL pts with unfavourable evolution during 1st line therapy are important to identify these rare cases of Seq Ly. The best salvage treatment should be defined and biological studies are warranted to decipher the pathogenesis, especially the clonal evolution of these Seq Ly.
Ghesquières: Celgene and Mundipharma: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Research Funding. Stamatoullas: Takeda: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation: Honoraria. Cartron: Celgene: Consultancy, Employment; Sanofi, BMS, Jansen, celgene, Roche, Gilead: Equity Ownership; Roche: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Honoraria, Research Funding. Karlin: Janssen: Honoraria, Other: Travel expenses. Salles: Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MSD: Consultancy, Honoraria; Morphosys: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Sarkozy: ROCHE: Consultancy; ROCHE: Honoraria; GILEAD: Honoraria; TAKEDA: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal